With Docker you can quickly and easily install, configure and use Selenium Grid. This tutorial shows the respective steps that you need as a software tester (or Developer). Instead of Python you can also use other languages, which are supported by Selenium.
Preconditions
Preparation of files
# create new project
$ mkdir -p ~/Project/SeleniumTutorial && cd ~/Project/SeleniumTutorial
# create docker-compose.yml (version 1)
$ vim v1-docker-compose.yml
# or create docker-compose.yml (version 2)
$ vim v2-docker-compose.yml
# create python example.py
$ vim example.py
Note: You can opt for a version of docker-compose.yml!
Version: 1
---
selenium_hub:
image: selenium/hub
ports:
- 4444:4444
node_1:
image: selenium/node-chrome
links:
- selenium_hub:hub
node_2:
image: selenium/node-firefox
links:
- selenium_hub:hubVersion: 2
---
version: '2'
services:
selenium_hub:
image: selenium/hub
ports:
- 4444:4444
node_1:
image: selenium/node-chrome
depends_on:
- selenium_hub
environment:
- HUB_PORT_4444_TCP_ADDR=selenium_hub
node_2:
image: selenium/node-firefox
environment:
- HUB_PORT_4444_TCP_ADDR=selenium_hub
depends_on:
- selenium_hubimport os
import datetime
import time
import unittest
from selenium import webdriver
class Example(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
self.driver = webdriver.Remote(
command_executor='http://192.168.99.100:4444/wd/hub',
desired_capabilities={
'browserName': 'firefox',
'javascriptEnabled': True
}
)
self.driver.get('http://softwaretester.info/')
def test_something(self):
dt_format = '%Y%m%d_%H%M%S'
cdt = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(time.time()).strftime(dt_format)
current_location = os.getcwd()
img_folder = current_location + '/images/'
if not os.path.exists(img_folder):
os.mkdir(img_folder)
picture = img_folder + cdt + '.png'
self.driver.save_screenshot(picture)
def tearDown(self):
self.driver.quit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main(verbosity=1)
Create environment
# create new VM
$ docker-machine create -d virtualbox Grid
# pointing shell
$ eval $(docker-machine env Grid)
# show status (optional)
$ docker-machine ls
...
NAME ACTIVE DRIVER STATE URL SWARM DOCKER ERRORS
Grid * virtualbox Running tcp://192.168.99.100:2376 v1.11.1
# run docker-compose (Version: 1)
$ docker-compose -f v1-docker-compose.yml up -d
# run docker-compose (Version: 2)
$ docker-compose -f v2-docker-compose.yml up -d
# show status (Version: 1)
$ docker-compose -f v1-docker-compose.yml ps
...
Name Command State Ports
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
seleniumtutorial_node_1_1 /opt/bin/entry_point.sh Up
seleniumtutorial_node_2_1 /opt/bin/entry_point.sh Up
seleniumtutorial_selenium_hub_1 /opt/bin/entry_point.sh Up 0.0.0.0:4444->4444/tcp
# show status (Version: 2)
$ docker-compose -f v2-docker-compose.yml ps
...
Name Command State Ports
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
seleniumtutorial_node_1_1 /opt/bin/entry_point.sh Up
seleniumtutorial_node_2_1 /opt/bin/entry_point.sh Up
seleniumtutorial_selenium_hub_1 /opt/bin/entry_point.sh Up 0.0.0.0:4444->4444/tcpOpen Browser
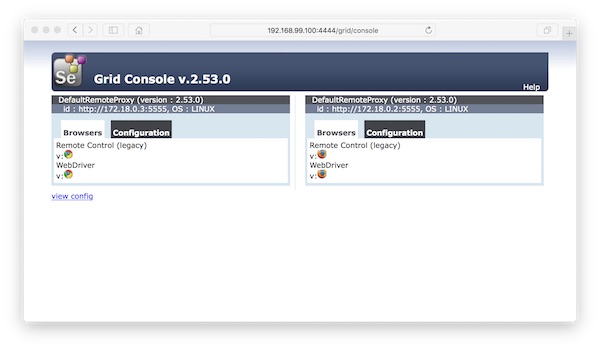
Run Python script
# run python selenium script
$ python -B ~/Projects/Selenium/example.py
Note: Via browserName (example.py) you can choose the respective browser (firefox or chrome)!
Note: Via docker-compose scale you can add/remove node instances!
# create 2 instances (Version: 1)
$ docker-compose -f v1-docker-compose.yml scale node_1=2
# create 3 instances (Version: 2)
$ docker-compose -f v2-docker-compose.yml scale node_2=3
